-
-
W-199-E, MIDC Khairne, Thane Belapur Road, Navi Mumbai – 400705. India.
Nilsan Nishotech —
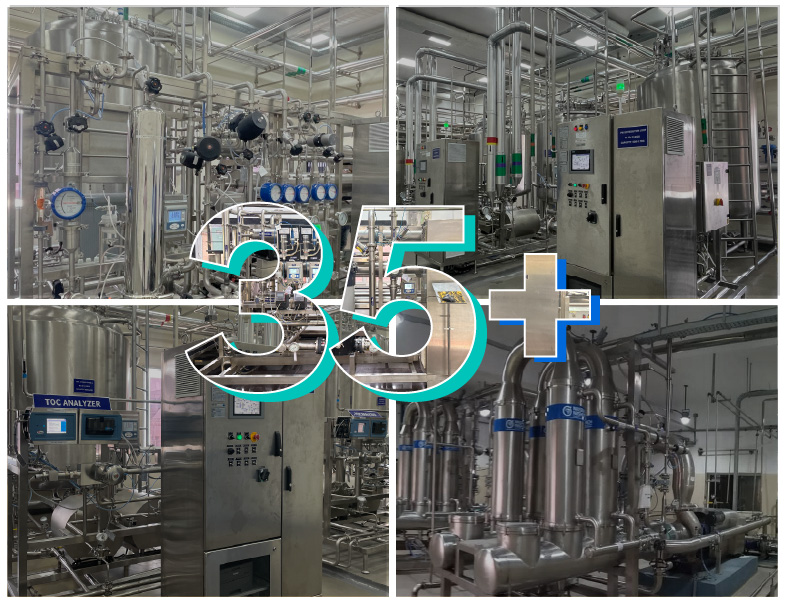
35+ Years of Engineering Excellence
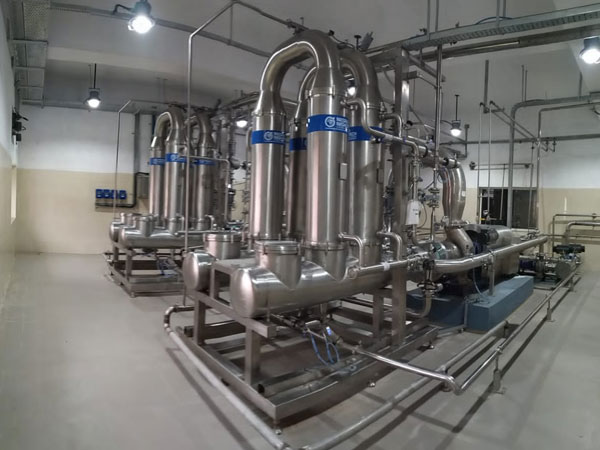
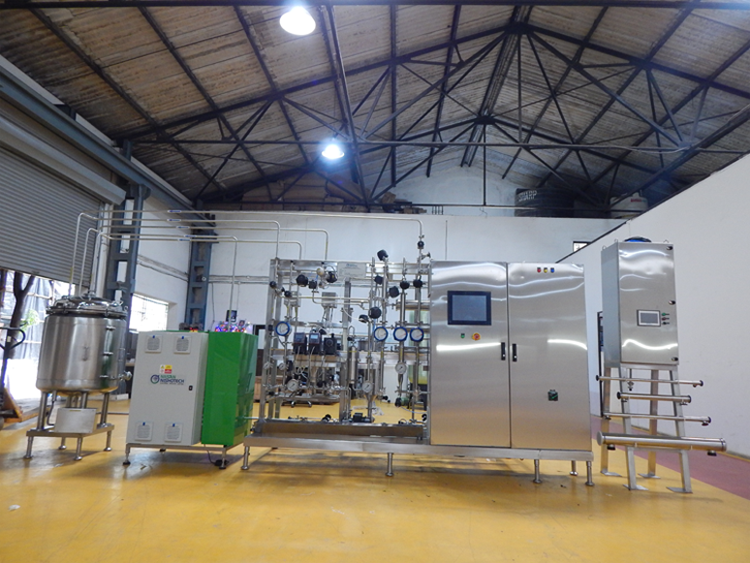
Nilsan Nishotech has come a long way since its humble beginnings nearly three decades ago and established itself as India’s most trusted engineering solutions provider. Over the years, we have grown from strength to strength and solidified our position as a reliable brand providing innovative high-purity water systems, custom-built solutions.
-
ISO 9001 & 45001 Certified
-
Global Execution | Local Expertise
-
Fully Automated | cGMP Compliant Systems
Our Core Capabilities
Our commitment to quality and maintaining delivery schedules coupled with world-class technologies. Our commitment to quality and maintaining delivery schedules coupled with world-class technologies and vast experience has enabled us to carve out a niche for ourselves.

Industries We Serve
Pharmaceutical
We design high-purity water and process systems that meet global pharma standards, ensuring consistency, reliability, and compliance.
BioPharmaceutical
Our scalable membrane and chromatography solutions support biologics, vaccines, and biosimilars with integrity and global compliance.
Electronics
We provide ultra-pure water systems for electronics and semiconductor firms, delivering precision, durability, and sustainable performance.
FMCG
Our process water and purification systems help FMCG brands maintain hygiene, efficiency, and safety.
Strength in Numbers


00
+Countries Served


00
+Projects Delievered


00
+Custom Technologies


00
+Industry Awards
Why Choose Us
-
Cleanroom FAT Facility
-
21 CFR Part 11 & GAMP 5 Compliance
-
AMC & Lifecycle Support
-
Process Validation (DQ, IQ, OQ)

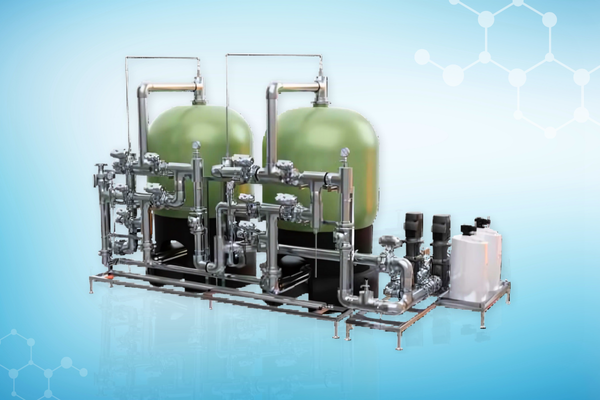
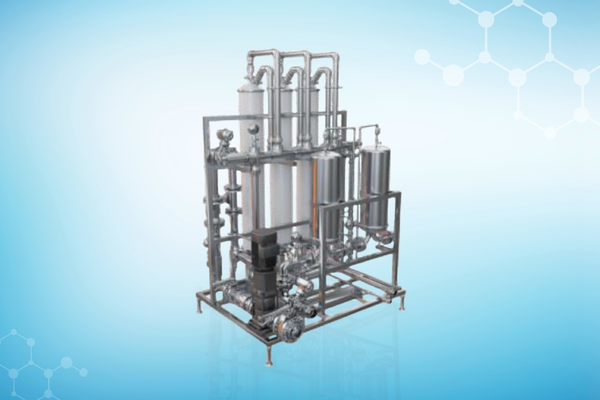
Our Solutions
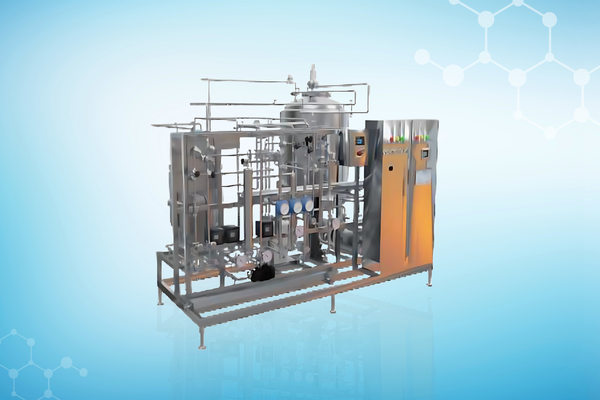
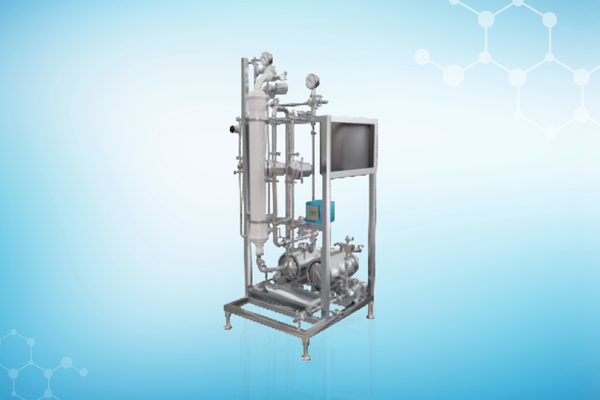
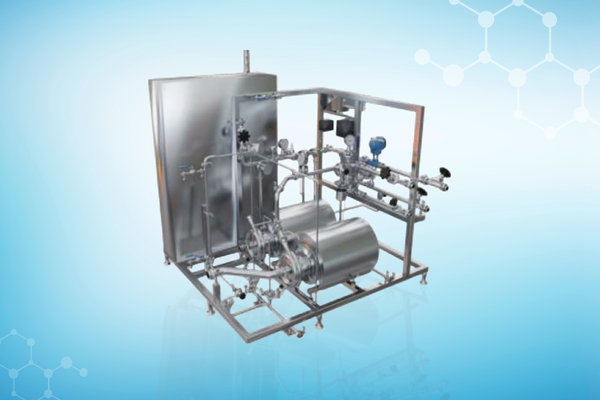
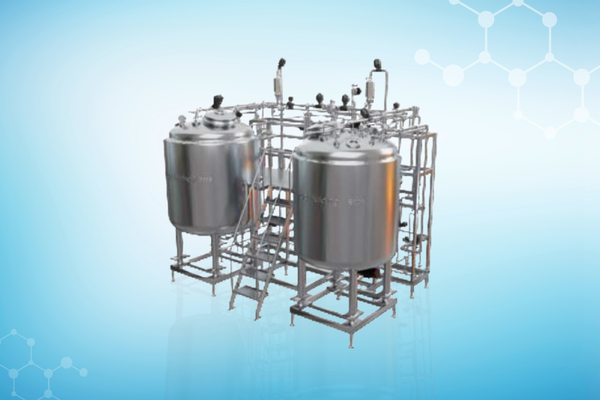
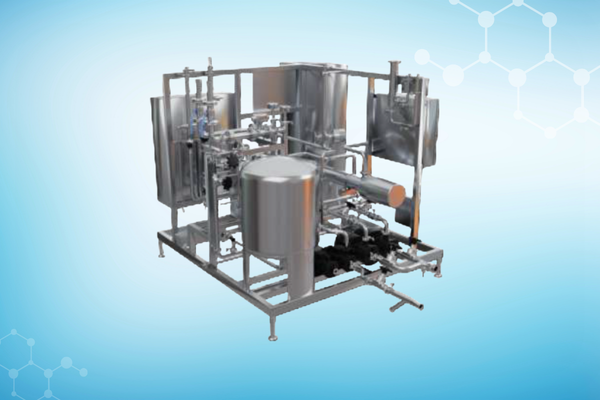
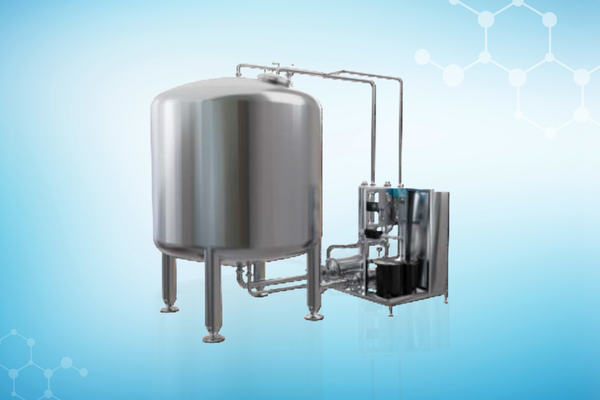
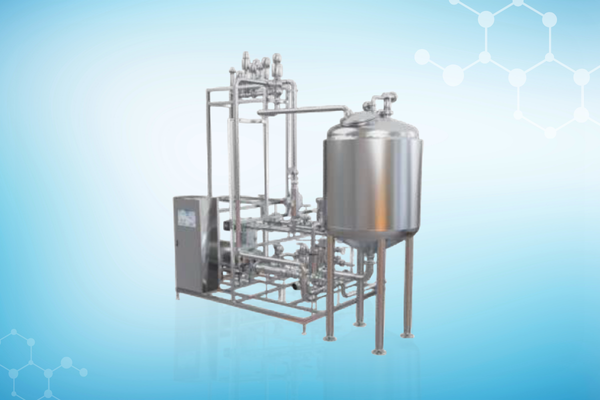
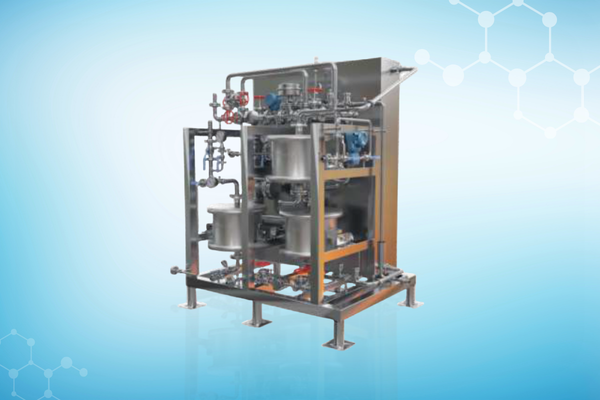












Recognition Awards and Certifications
Nilsan Nishotech has evolved into India’s most trusted engineering solutions provider, serving prominent clients with a commitment to quality, timely delivery, and cutting-edge technologies.

Recipient of SME Excellence Award

Best Strategic Partner by ABBOTT India

Maharashtra Rajya Gaurav Chinah for noteworthy contribution in small scale Industry sector

Reliance National Safety Week Award

ISO 9001:2015
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM

ISO 45001:2018
SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM

Colgate Palmolive Safety Award

Sanofi Safety Excellence Award
Our Clientele
Customers in 25+ countries that are highly pleased and have a significant amount of trust.





















